TABLE OF CONTENTS
Surgical affections of Cornea
Surgical affections of Cornea of eye in animals are Keratitis, Corneal ulcer and Opacity of Cornea.
Surgical affections of Cornea are-
- Keratitis
- Corneal ulcer
- Opacity of Cornea
- Cataract (Surgical affection of lens)
Keratitis
Keratitis is nothing but the inflammation of the cornea of eye.
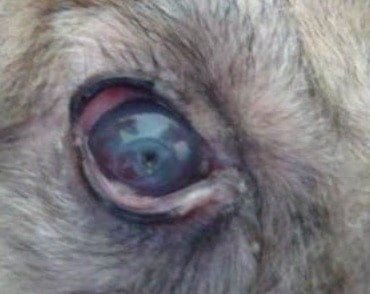
Keratitis in a dog
Etiology
- Bacterial, virual, rickettsial infections
- Trauma (including irritation caused by eyelashes, in entropion, trichiasis, distichiasis, etc)
- Chemical irritants
- Parasites in eye.
- Allergy
- Deficiency diseases (Vitamin A, Riboflavin, etc.).
- Senility (due to old age)
- Neoplastic conditions as dermoids.
- Toxaemia
- Diabetes
Classification
Keratitis may be classified as follows-
- Superficial keratitis
- Interstitial keratitis (parenchymatous keratitis)
- Vascular keratitis
- Ulcerative keratitis
- Suppurative keratitis
- Non-suppurative keratitis
The normal, clear, transparent, moist and glistening appearance of cornea is altered.
Symptoms
- Keratitis is a painful condition
- Photophobia and blepharospasm
- There is loss of lusture of the cornea.
- The transparency of the cornea is altered and cloudiness or opacity is evident.
- Vascularisation of the cornea (pannus) may be noticed in severe cases.
- The vessels invading the cornea may originate either from the superficial vessels of the conjunctiva or from the deeper ciliary vessels, situated at the limbus.
- Vessels originating from the conjunctiva are bright red, wavy and superficial whereas the ciliary vessels appear pale or bluish grey and have a more or less straight course. In chronic cases these vessels are arranged in a brich – broom fashion.
Treatment
- Remove the cause
- NSAIDS topically to relieve pain
- Irrigating with antiseptic solutions like 5% povidone iodine
- Adequate intake of vitamin A, D and B-complex
- Instilling topical antibiotics following a ABST
- Adminstration of antibiotics
Corneal ulcer
A corneal ulcer is an open sore in the outer layer of the cornea. Ulcerative keratitis is frequently met Corneal ulcer within animals.
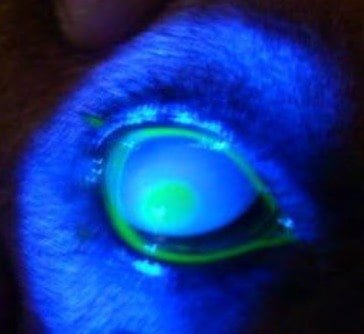
Fluorescein dye test positive corneal ulcer viewed through the cobalt filter of ophthalmoscope. The green colour in the center of the cornea indicates stain uptake by the corneal stroma.
Etiology
The causes may be trauma, infections (like distemper in dogs), or nutritional deficiencies (like vitamin A deficiency and Riboflavin deficiency).
Symptoms
The ulcer on the cornea is easily recognized. If necessary, a 2% flurorescein solution may be used to aid diagnosis. The solution is instilled into the eye so as to stain the ulcer and make it visible.
Prognosis
Prognosis is guarded and depends on how deep the ulcer is. When the ulcer heals a localized opacity of cornea results, because of the scar tissue.
Diagnosis
Fluorescein dye test
- Impregnated paper strips moistened with saline
- Placed in dorsal bulbar conjunctiva
- Excess stain is washed with normal saline
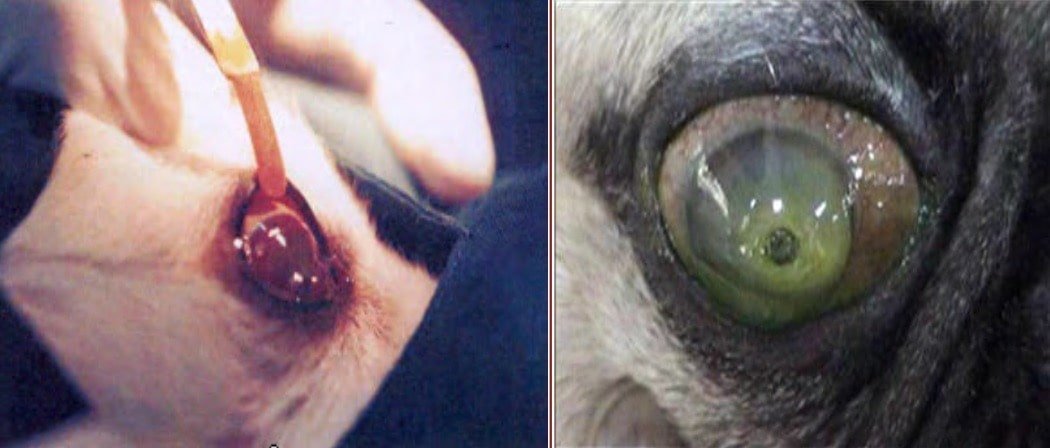
Complications of corneal ulcers
Keratocele
Keratocele is the protrusion of an intact decemet’s membrane through the ulcer. Keretocele may be rupture.
The rupture might help correction of the keratocele and the ulcer might heal up, if small. Rupture may predispose to prolapse of iris if the wound on the cornea is sufficiently large. So it is better to make a small puncture of the keratocele artificially to let out the aqueous humour and facilitate collapse of the protruded portion. The keratocentesis may be repeated, if necessary.
Staphyloma
Staphyloma is a protrusion of iris through a wound or ulcer on the cornea. There is leakage of aqueous humour and there is also chance of infection being carried through the perforation of the cornea. If the opening is large the lens may also prolapse. A small staphyloma resulting from a narrow opening in the cornea may slough off during the healing of the corneal wound.
Treatment of corneal ulcers
Surgical treatment is used to treat corneal ulcers in animals-
- Temporory tarsorrhaphy
- Third eyelid flap
- Conjunctival flap
- Direct corneal suturing
- Therapuetic contact lenses
- Collagen grafting
In addition to the surgical treatment, medical therapy is also indicated, which include topical antibiotics, collagenase inhibitors, atropine to prevent ciliary spasm, ocular lubricants, and systemic corticosteroids.
Opacity of Cornea
Opacity of cornea is one of the symptoms of chronic keratitis. In mild forms there will be only cloudiness which clears up once the inflammation subsides.
In chronic cases this opacity becomes permanent.
Classification
According to the degree of opacity, opacities of the cornea may be classified as-
- Severe
- Moderate
- Mild
- Normal
Treatment
Rule out Intra ocular pressure (IOP) rise.
Medical management
- Use of topical antibiotics and NSAIDS (Flurbiprofen) four times daily
- Use of saline irrigation
- Administration of placental extract, subconjunctivally
- Surgical management
- Superficial keratectomy
Cataract
Cataract is the most common surgical affection of lens of eye in animals. Opacity of the lens is known as cataract. It is a degenerative lesion of the lens.