TABLE OF CONTENTS
Ranitidine
Ranitidine or Ranitidine Hydrochloride is a H2 (Histamine-2) blocker that is used as an anti ulcer agent in animals and humans. Cimetidine, Famotidine, and Nizatidine also come into this group of medicine.
Pantoprazole and omeprazole (proton pump inhibitors) have better efficacy than ranitidine, but ranitidine can be used by almost all routes of drug administration, while pantoprazole can only be used by the IV and PO routes.
Ranitidine Vs Ranitidine Hydrochloride
Ranitidine is the active ingredient of the Ranitidine hydrochloride that is available in injection, tablet, etc. forms.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the United States asked manufacturers to remove all ranitidine medicines from the market in 2020. The FDA discovered that certain ranitidine products have N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA). This NDMA is a carcinogen for both humans and animals.
Group
Ranitidine is grouped into H2 Blockers and Anti Ulcer drugs.
Mechanism of Action
Ranitidine works by inhibiting the stimulation of gastric parietal cells. This inhibition leads to a reduction in gastric acid secretion (hydrochloric acid, or HCl) and an increase in stomach pH.
Dose Rates
Dose rate of ranitidine in Dogs: 2 mg/kg q8h IV SC IM PO
Dose rate of ranitidine in Cats: 2.5 to 3.5 mg/kg q12h IV SC IM PO
Dose rate of ranitidine in Horses: 2 to 6 mg/kg q6-8h IV SC IM PO
Dose rate of ranitidine in Cattle: 5 to 10 mg/kg q12h IV SC IM PO
Dose rate of ranitidine in Sheep & Goats: 1 to 2 mg/kg q12h IV SC IM PO
Indications
Ranitidine has been used to:
- Treat gastric and duodenal ulcers
- Treat gastritis
- Treat reflux esophagitis
- Prevent NSAIDs induced ulcers
Contraindications
- Avoid the use of ranitidine in pregnancy, lactating animals, and patients with renal disorders.
Interactions
Ranitidine interferes with the oral absorption of drugs dependent on acidity, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and iron supplements.
Adverse effects
Ranitidine products that have high levels of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) are potential carcinogens and should not be used.
Toxicity
Central nervous system (CNS) signs may occur with high doses of ranitidine.
Preparations
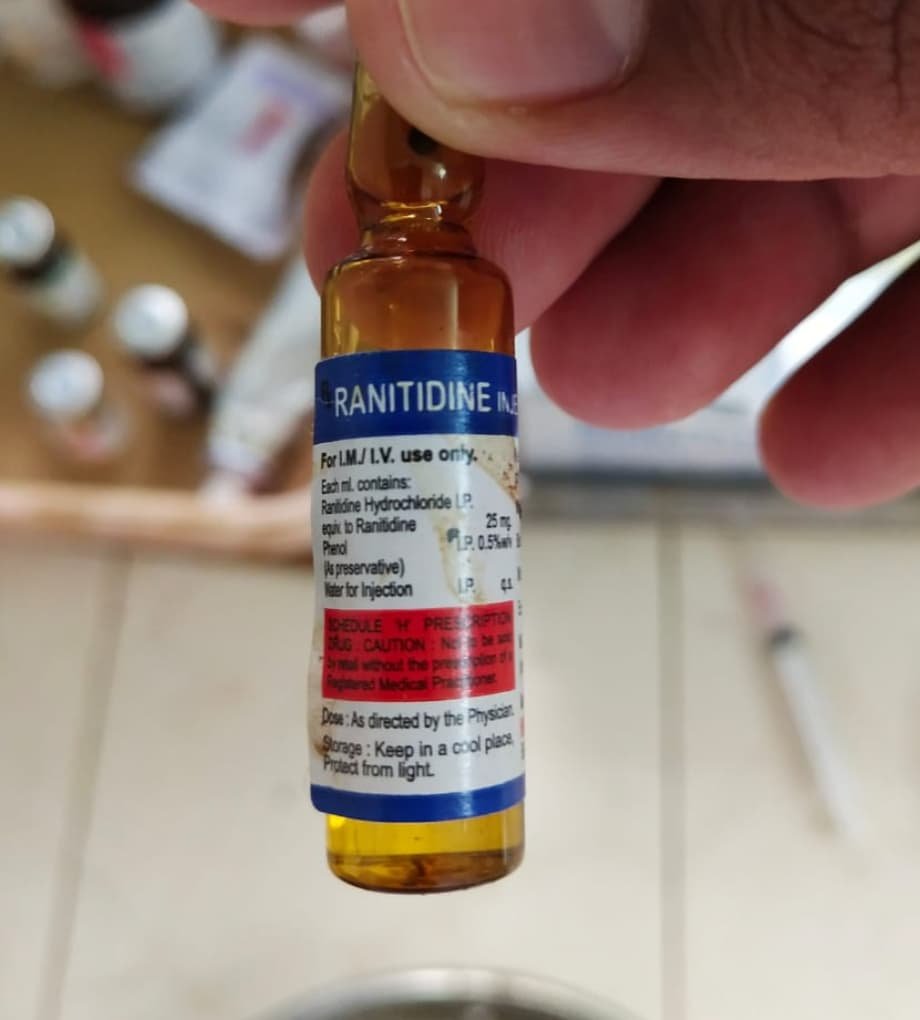
Ranitidine hydrochloride is available in injections, tablets, and capsule forms.
Ranitidine hydrochloride Injection preparations:
- Inj. RANTAC 25 mg/ml concentration in a 2 mL ampoule
- Inj. ACILOC 25 mg/mL concentration in a 2 ml ampoule
- Inj. HISTAC 25 mg/ml concentration in a 2 mL ampoule
- Inj. R-LOC 25 mg/ml concentration in a 2 mL ampoule
Ranitidine hydrochloride tablet preparations:
- Tab. RANTAC (150mg, 300mg)
- Tab. ACILOC (150mg, 300mg)
- Tab. HISTAC (150mg, 300mg)
More about Ranitidine for animals
Information provided here may be subject to inaccuracies. Please consult a reputable textbook for verification before use. We welcome your feedback and suggestions for improvement via email at hello@vetscraft.com

