Pineal gland physiology
Pineal gland is the main translator of photoperiodic effect in animals. The pineal gland produces a hormone, melatonin in response to darkness. Light passes from the retina to supra chiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus, superior cervical ganglia and to pineal gland.
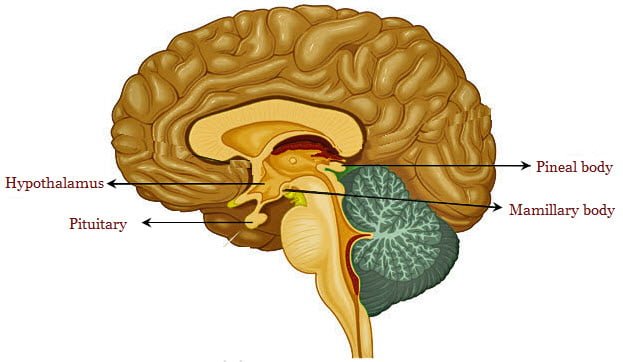
The melatonin inhibits gonadal activity.
Cat and horse are positively affected with increasing light period and goat and sheep are positively affected by decreasing photoperiod.
The pineal gland acts to relay light-dark information to the hypothalamus and regulates seasonal breeding in animals.