TABLE OF CONTENTS
Peripheral nervous system or PNS
Peripheral nervous system or PNS includes all nervous structures, the peripheral ganglia, spinal nerves, cranial nerves and the autonomic nerves, located out of the brain and the spinal cord.
It functions to provide communication between the receptor organ and the CNS (sensory), from the CNS and the effector organs (motor). Peripheral nerves are myelinated.
It is divided into motor (efferent) and sensory (afferent) subsystems.
The motor peripheral nerves that supply to skeletal muscles are referred to as somatic motor nerves and those that supply the cardiac and smooth muscles and exocrine glands are referred to as autonomic nerves.
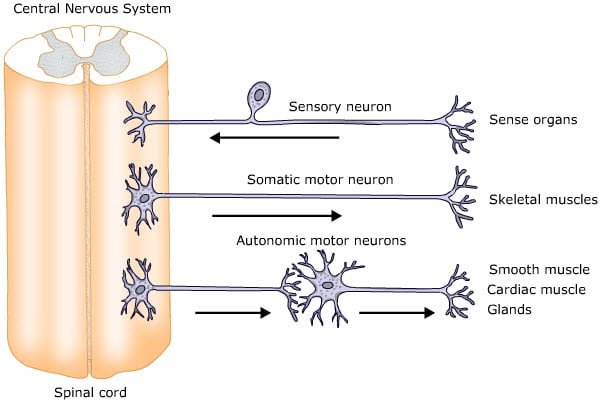
The afferent (sensory) system is of two types: Somatic and visceral.
Somatic sensory nerves carry impulses from the photoreceptors (eye), auditory receptors (ear) and stretch receptors (skeletal muscles), whereas the visceral sensory nerves carry visceral sensations from the chest and abdomen.
Somatic components
The spinal nerves emerge as a pair of nerves from each spinal segment through the inter-vertebral foramina, which lies between the two adjoining vertebrae. Thus, the number of pairs of thoracic, lumbar and sacral nerves is similar to the respective vertebrae.
Although the cranial portion has seven cervical vertebrae, eight pairs of cranial nerves emerges, while the caudal vertebrae have fewer pairs of coccygeal nerves. The terminal portion of the spinal cord, the meninges and the nerves are collectively referred to as cauda equinae.
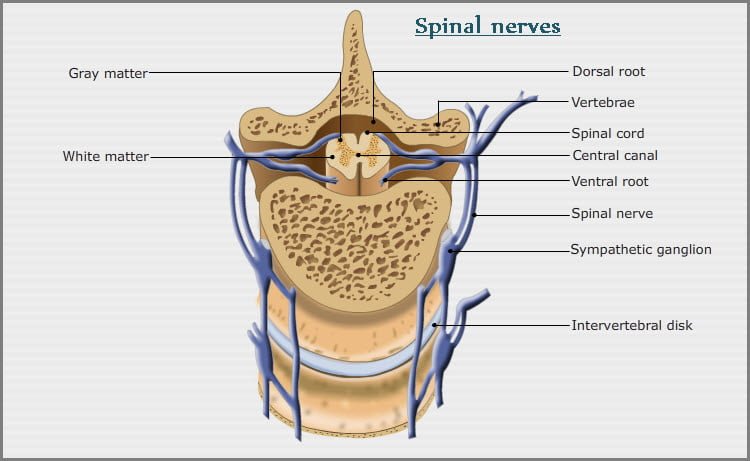
The dorsal spinal root is the afferent neuron and it propagate sensory impulses from the periphery towards spinal cord and the cell bodies of these neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglion.
The somatic motor nerves or the efferent nerves emerge from the cell bodies of ventral roots, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. Both the dorsal and ventral roots unite to form the spinal nerves that emerge through the inter-vertebral foramen.
Thus, the spinal nerves are mixed nerves, containing both sensory and motor fibres. However, outside the vertebral canal it divides into dorsal and ventral branches.
The nerves from the last three cervical and the first one or two thoracic nerves form a net work, the left and the right brachial plexus‚ supply to the respective fore limbs.
The ventral branches of the last 3 to 5 lumbar and first 2 to 3 sacral nerves unite to form the right and left lumbo-sacral plexus, supplying to the respective hind limbs.
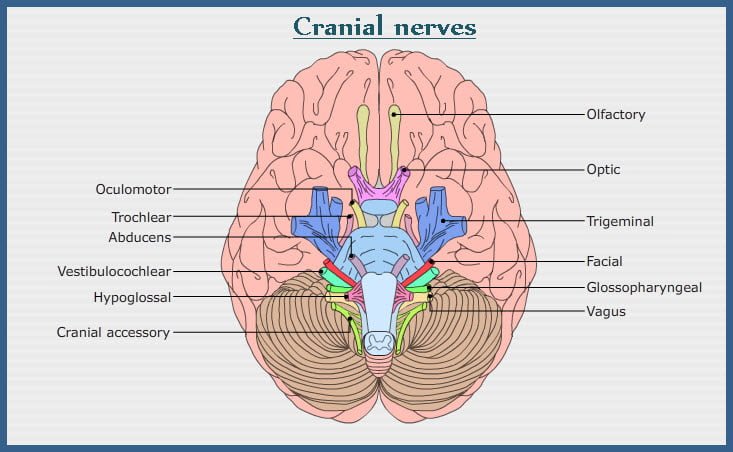
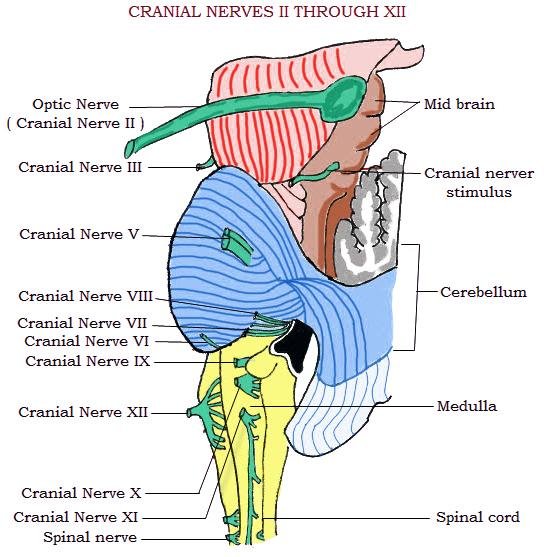
Cranial nerves
Twelve pairs of cranial nerves emerge through the foramina of the skull; hence they do not have dorsal and ventral roots. Some of the cranial nerves are purely sensory and some are strictly motor in function, while some nerves are mixed in functions.