TABLE OF CONTENTS
Nasal Cavity of different Animals
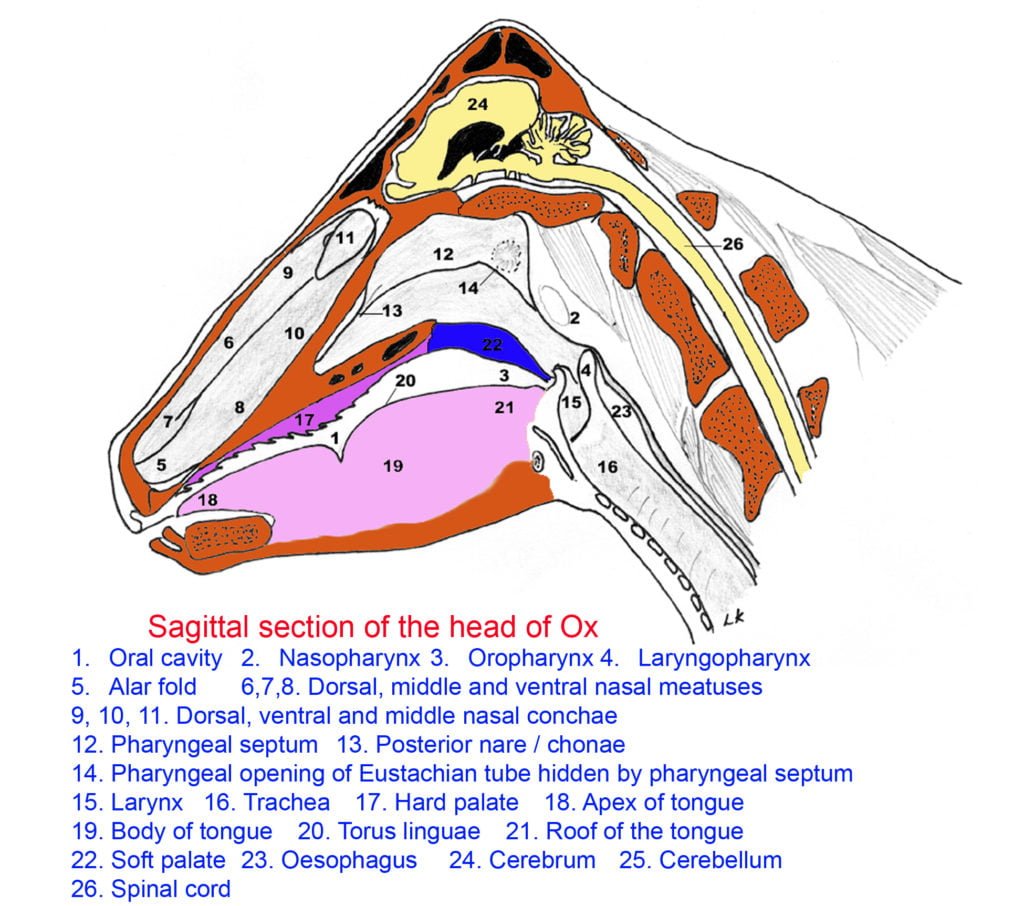
The nasal cavity is the first section of the respiratory tract. It is a short tubular passage, wide in front and narrow behind, enclosed by the facial bones.
Nasal Cavity of Ox
- Nasal Cavity of Ox is separated from the mouth by the palate and opens in front at the cranial nares or nostrils and caudally it opens into the pharynx through the caudal nares.
- The nostrils (nares) are two-left and right and are somewhat oval in outline and are placed obliquely so that they are closer together below than above
- They are situated at either end of the muzzle. They are bounded by twoalae or wing and cranial part of the cartilaginous septum.
- The alae meet above and below forming commissures
- The superior commissure is narrow and the inferior one is wide and rounded
- The lateral alae are concave and medial one is convex above and concave below. The prominence of the medial alae is caused by the lamina of the alar cartilage
- The alar cartilage forms the dorsal wall by its lamina and the lateral wall by its cornua and a transverse bar looks like an anchor
- The medial wall is formed by the nasal septum.
- The skin on the dorsal and lateral wall is covered by hairs and the skin between and around the lining of the nostrils is devoid of hairs and is smooth, bare and moist
- There is no clear line of demarcation between the skin and nasal mucosa.
- The nasal cavity is short wide cranially and narrow behind. The nasal cavity is divided into two halves by an osseo-cartilaginous septum nasi
- The osseous part is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid, vomer and the cartilaginous part by the septal cartilage
- The surfaces of the cartilage form the internal walls of the nasal cavity
- The dorsal border is attached along the frontal and nasal sutures and extends beyond the apices of the nasal bones about two inches
- The nasal cavity is not completely divided by the septum nasi due to the fact that the caudal third of septum nasi is separated from the floor of the nasal cavity by an interval that increases from before backward
- The cavity is mostly occupied by the nasal and ethmo-turbinates
- It is divided into three passages or meatuses called as dorsal, middle and ventral nasal meatus.
- The dorsal nasal meatus is a narrow passage between the roof of the nasal cavity and the dorsal turbinate bone
- Its caudal end is closed by the junction of the inner plate of the frontal bone with the cribriform plate and lateral mass of the ethmoid. It transmits air to the olfactory region.
- The middle nasal meatus is between the dorsal and ventral turbinate bones
- It is a very narrow passage and divides caudally into two branches by the intervention of the ethmoturbinates
- The ventral nasal meatus is situated between the ventral turbinate and the floor of the nasal cavity
- It is much larger than the other two and is the direct passage between nostrils and pharynx
- The opening of the vomero-nasal organ and incisive or naso palatine duct is situated in the floor of the cranial end of this meatus
- The common nasal meatus is situated between the nasal septum and the turbinates and is continuous laterally with the other meatuses. It is narrow dorsally but wider ventrally.
- The caudal nares or chonae are elliptical openings by which the nasal cavity and the pharynx communicate and situated in the same plane on the floor of the nasal cavity at its caudal extremity and are separated by the vomer.
- The nasal cavity is lined by mucous membrane, which is highly vascular
- In front, it is continuous with the skin lining the nostrils and behind with the mucous membrane of the pharynx
- The lower three-fourth of the mucous membrane is red in colour and forms the respiratory portion
- The upper fourth paler part forms the olfactory portion, which is responsible for smell.
- The ductus incisivus (naso-palatine duct) is a small mucous tube, which extends from the nasal cavity to the papilla incisive
- The nasal opening of this duct opens on the medial surface of the alar fold of the ventral nasal meatus
ORGAN OF JACOBSON
The vomero-nasal organ (organ of Jacobson) is a cartilaginous tube situated on the floor of the nasal cavity on either side of the ventral border of the septum nasi in its cranial third. They open on the oral cavity on either side of the papilla incisiva along with those of the ductus incisivus. The caudal end is blind.
Nasal Cavity of Sheep and Goat
Generally Nasal Cavity of sheep and goat resembles ox with little modifications. The nostrils are nearly horizontal slits. The ductus incisivus is short.
Nasal Cavity of Horse
- The nasal cavity is longer and cylindrical
- The nostrils are very dilatable and are divided by the alar fold into a small blind diverticulum on the upper part -the false nostril and a large lower part – true nostril
- The naso-lacrimal orifice is visible on the floor of the true nostril about 2″ behind the inferior commissure
- The ductus incisivus is blind at its dorsal end
Nasal Cavity of Pig
The nostrils are situated in the flat cranial surface of the rostrum or snout, a short cylindrical projection with which the upper lip is fused and is circumscribed by a prominent circular margin.
The nostrils cannot be dilated much because they are embedded within the skeleton of the face. The nose is extended from the snout to the level of the eye.
In the snout, a bone, os rostri between the nostrils is seen as an adaptation to the habit of burrowing or rooting
The skin covering the snout is pigmented and divided by shallow grooves. These surface markings are specific for individual animals and helpful in identification. The nasal cavity is long and narrow. The incisive duct and vomero-nasal organ are as in ox.
Nasal Cavity of Dog
The nostrils of dog are comma-shaped.

The nasal cavity of dog varies greatly in different breeds. It is almost completely occupied by the turbinate bones
Nasal Cavity of Rabbit
The nostrils of rabbit are in the form of elongated slits between the nasal flap and the upper jaw. The nasal bones are well built and the nasal cavities are extended.
Nasal Cavity of Fowl
The nostrils of fowl are two narrow oval openings placed at the base of the upper beak and these are cartilaginous.
The cavity opens into the mouth and pharynx by a long narrow slit like opening. The dorsal border of the nostrils are bounded by a small piece of horny skin-the operculum.

