Juxtaglomerular apparatus or JG apparatus
When the thick segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle returns to its glomerulus of origin in the cortex, it passes in the angle between afferent and efferent arterioles and continues as the distal tubule. The side of the tubule that faces the glomerulus comes in contact with the arterioles, the contact epithelial cells are more dense than the other epithelial cells and are collectively called as macula densa. Macula densa marks beginning of the distal tubule.
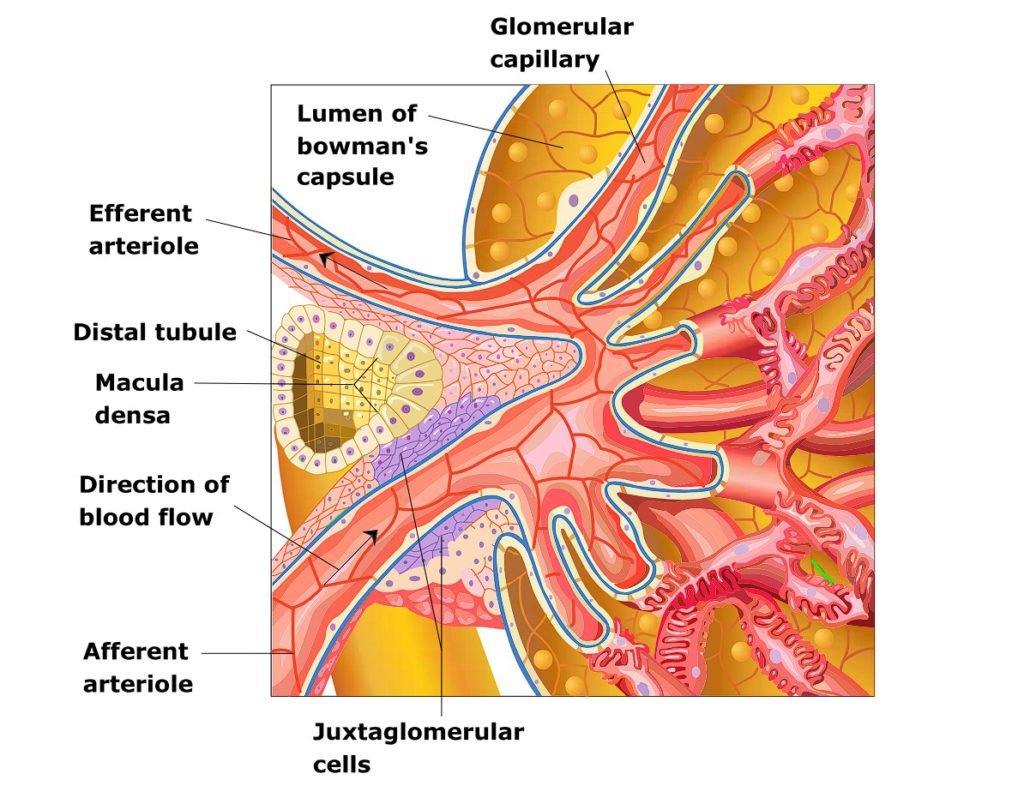
The smooth cells of the afferent and efferent arterioles that make contact with the macula densa are specialized smooth muscle cells and are called as Juxta glomerular cells or Granular cells. Juxta glomerular cells have secretory granules that contain renin, a proteolytic enzyme.
The space between the macula densa and the afferent and efferent arterioles and the space between the glomerular capillaries is known as mesangial region/Extra glomerular mesangial cells or Lacis cells.
JG cells are involved in feed back mechanism that assist regulation of renal blood flow and glomerular filtrate rate.