A common trunk (Intra-thoracic branch) arises from the dorsal face of the artery close to its origin and soon divides into subcostal, dorsal or costo-cervical, deep or superior cervical and vertebral arteries.
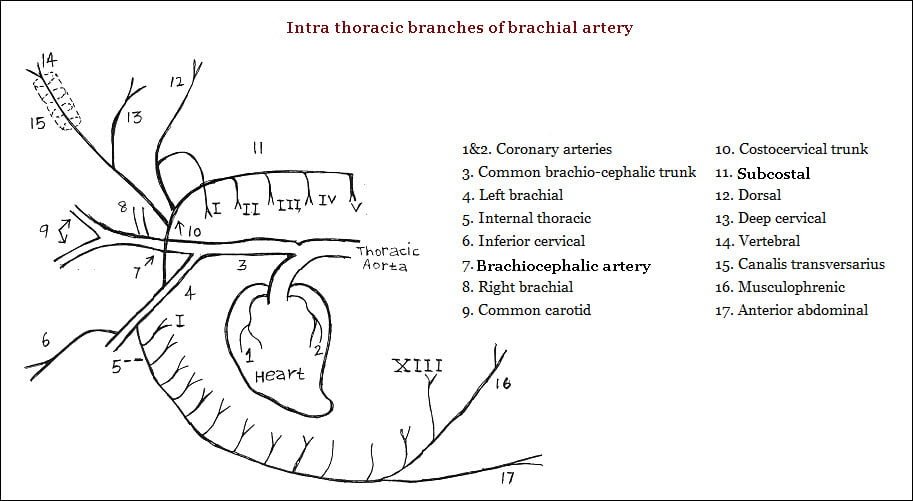
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Subcostal artery
- The subcostal artery arises from the dorsal artery or from the common trunk.
- It passes upwards and backwards along the ventral aspect of the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae and gives off the second to the fifth intercostal arteries.
Dorsal artery
- The dorsal artery is small.
- It leaves the thoracic cavity by passing in front of first costotransverse articulation.
- It gives off the first intercostal artery.
- It then passes deeply into the substance of the serratus cervicis and supplies splenius, complexus, rhomboideus, serratus cervicis and trapezius.
Deep cervical artery
- The deep cervical artery arises usually outside the thorax from the superior face of the vertebral artery about the level of the transverse process of the seventh cervical vertebra.
- It passes on the deep face of the complexus and supplies all the muscles of the lateral cervical group, ligamentum nuchae and skin.
Vertebral artery
- The vertebral artery is large.
- They are each on either side. Each emerges out of the thorax between the scalenus and longus colli, passes under transverse process of the seventh cervical vertebra, detaches the superior cervical artery, then enters the foreman transversarium of the sixth cervical vertebra passes through the series of foramina transversarius of the cervical vertebrae with its satellite vein and nerves covered by the intertransversales colli, reaches the intervertebral foramen between the second and the third cervical vertebrae detaches a thick muscular branch and enters the spinal canal.
- It runs forwards on the floor of this canal and divide in the ring of atlas into two branches, medial and lateral.
- The medial branch or cerebrospinal artery passes on the cranial floor and joins the rete mirabile cerebri a vascular network around the pituitary gland. Several anastomoses with the opposite artery are present.
- The larger lateral branch contributes a twig to the rete mirabile, emerges out through the intervertebral foramen of atlas and supplies the muscles in this region. The vertebral artery in its course gives branches to the intertransversales colli and opposite to each intervertebral foramen a spinal branch to the spinal cord and its meninges.
- The spinal branches enter the spinal canal and reinforce the ventral spinal artery on the ventral face of the spinal cord.

