TABLE OF CONTENTS
Functions of limbic system
Limbic System
Limbic system consists of cortical and subcortical areas which are structurally and functionally related to forebrain. It forms a ring of forebrain structures that surround the brainstem and are interconnected by intricate neural pathways.
The components of the limbic system are hippocampus, amygdala and cingulate gyrus.
It is concerned with emotions and visceral functions viz. VISCERAL BRAIN. It helps out in basic survival and sociosexual behavioral pattern. The subcortical relay nuclei comprises of septal nuclei, mammillary bodies, medial and lateral hypothalamic nuclei associated with limbic system.
Functionally, it includes lobes of cerebral cortex, basal nucleus, thalamus, and hypothalamus.
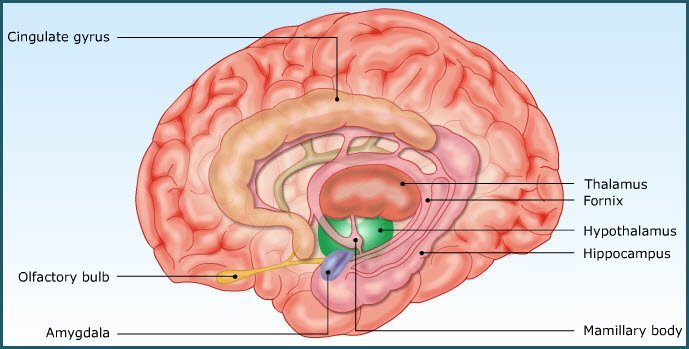
Limbic system has certain areas designated as ‘reward and punishment’ centres which functions in the programmed way based on the previous experiences. Limbic system is not well defined in birds.
Functions of limbic system
- Limbic system is the neural substrate for emotional experience and expression through somatic and visceral changes.
- Limbic system is involved in 3 levels of behavior.
- Drive
- Emotions.
- Goal directed behavior. (Motivation: It is the ability to direct behaviour towards specific goals and is called as goal direct behaviour.)
- Expression of drive is concerned with rhinal system comprising of amygdala, prepyriform cortex and septal nuclei. Emotional behavior is mediated via hippocampus. Goal directed behavior is mediated by cingulate gyrus, prefrontal cortex, and the hypothalamic structures.
- Visceral automatic control: Regulation of BP, respiratory and vasomotor mechanism.
- Olfactory processing.
- Neuro-endocrine control.
- Formation of memory process (Short-term-Long term memory by hippocampus)