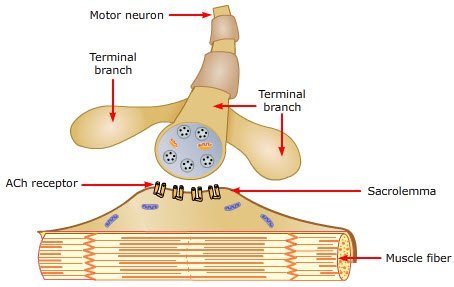
Functional anatomy of the synapse
A typical motor neuron (efferent neuron) shown under electron microscope numerous (average about 6000) small knobs spread over the surface of the dentrites (80-90%) and soma (10-20%). These knobs are the ends of nerve fibrils that have their origin in many other neurons (usually not more than a few derived from any single previous neuron). The knobs are referred to as presynaptic terminals or terminal knobs, buttons, end feet and synaptic knobs.
- Neurons in other parts of the cord and brain differ markedly from the motor neuron in the following features-
- Size of the soma
- Size, length and number of dentrites (ranging in length as long as many centimeters)
- Size and length of axon
- The number of presynaptic terminals (range from few to more than one hundred thousand).
These differences are responsible for the neurons of the different parts of the nervous system to react diversely to incoming signals in their functions.