TABLE OF CONTENTS
Contrast radiography techniques
There are many Contrast radiography techniques in animals and the following are some of the important contrast techniques-
- Barium Series
- Barium Enema
- Barium Swallow (Esophagography)
- Reticulography
- Pneumoperitoneography
- Arthrography
- Intravenous Pylography
- Mylography
These all Contrast radiography techniques are explained below-
1. Barium Series
Barium Series procedure is indicated to evaluate the structural and functional status of the gastrointestinal tract in small animals. It should be avoided if rupture of the stomach or intestine is suspected.
Technique of Barium Series in Calves, Sheep & Goats
- Keep the animal off feed for 36 hours and off water for 12 hours
- Administer 0.5 kg Magnesium sulphate orally 24 hours before the study
- 100 grams of activated charcoal given orally 12 hours before, to clear the gas in Gasto-intestinal tract
- Give warm soap-water enema to clear the bowel
- Administer 70% solution of barium sulphate at 25-30 ml/kg orally
- Obtain lateral (L) and ventrodorsal (VD) projections at various intervals
The entire course of intestine is not visualised at one time. Most organs upto cecum are visualised at 4 hours, while colon gets demarcated between 6-8 hours, after administration. In case of dogs, the barium sulphate 15- 20% is used at 6-12ml/kg and the laxatives are not used.
2. Barium Enema
Barium enema is indicated to outline the colon and rectum to rule out intramural or extraluminal obstructions. It should not be used if perforation is suspected.
Technique of Barium Enema in animals
- Keep the animal off feed for 36 hours and off water off water for 12 hours
- Give magnesium sulphate orally before 12 hours as a laxative
- Give warm soap- water enema 2hours before
- Sedate the animal deeply after controlling it in lateral recumbency
- Raise the hind quarters for retention of contrast agent in the gut
- Insert cuffed lubricated catheter into the rectum and inflate it
- Administer micropulvarised barium sulphate 15-20% at 15-20ml/kg
- Obtain right lateral and ventrodorsal projections
- Evacuate the contrast materials from the gut by elevating the cranial part of the abdomen
3. Barium Swallow (Esophagography)
The Barium Swallow (Esophagography) Contrast radiography techniques in animals is used to evaluate both structural and functional status of the esophagus after introduction of positive contrast agent.
Indications of Barium Swallow (Esophagography)
- Esophageal obstruction
- Esophageal stenosis
- Esophageal diverticulum
- Esophageal perforations
- Esophageal mucosal diseases
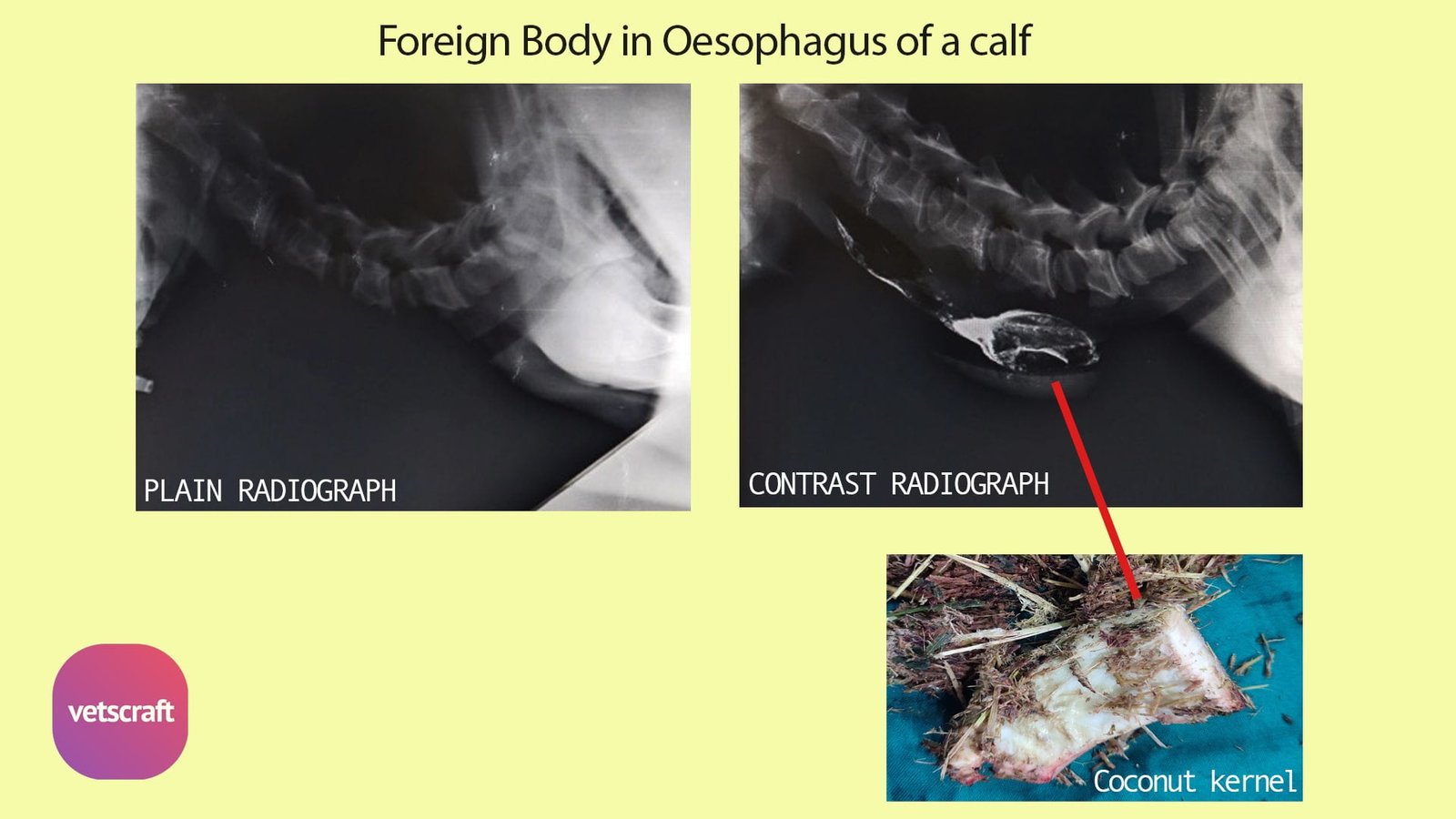
Barium Swallow should not be used if rupture of the thoracic part of esophagus is suspected.
Technique of Barium Swallow
- First obtain a survey radiograph of the area.
- Prepare barium suspension in water with the viscosity of light cream.
- Administer orally the barium swallow slowly (1-2ml / kg)
- Make lateral radiograph of esophagus at the last swallow.
Appearance of Barium Swallow
In the absence of obstruction, the mucosal folds appear as linear streaks. In case of obstruction, barium gets accumulated cranial to the obstruction site. Diverticulum is identified as an esophageal out pouch filled with contrast agent.
Double and Triple Contrast radiography techniques in animals
Double contrast is a radiographic contrast study technique, in which uses the combination of positive and negative contrast media simultaneously. The positive contrast material is administered initially followed by negative contrast material.
Triple contrast radiography: Infusing air into peritoneal cavity and obtaining pneumoperitoneum and then administering double contrast to Rectum and colon obtain triple contrast radiography.
4. Reticulography
Reticulography technique is indicated to diagnose, reticular hernia in bovines.
Technique of Reticulography in animals
- Keep the animal off feed for 24 hours and off water for 12 hours
- Administer orally thick barium suspension (1-2kg)
- Restrain the animal in lateral recumbency
- Take a lateral radiograph after 40 minutes
Reticulography helps to differentially diagnose diaphragmatic hernia from pleurisy and pherinic abscess.
5. Pneumoperitoneography
Pneumoperitoneography is the radiographic study of the peritoneal cavity and its contents after introduction of a negative contrast agent. If barium series and pneumoperitoneum are combined it is called double contrast peritoneography. These are indicated to visualize outline of various abdominal organs. It should not be used if diaphragmatic hernia is suspected because of the risk of pneumothorax.
6. Arthrography
Arthrography is used to visualize structures of a diarthrodial joint after injecting a positive or negative contrast medium or a combination of both. It is indicated to diagnose various joint abnormalities.
7. Intravenous Pylography
Intravenous pylography refers to the contrast radiographic examination of the kidneys and ureters after intravenous introduction of a positive contrast agent like iothalmate. It will also give a rough index of kidney function. It is contraindicated in severely dehydrated patients.
8. Mylography
Mylography technique refers to the contrast radiographic examination of the spinal cord and emerging spinal roots after injecting the contrast material, the metrizamide into the subarachinoid space. It is indicated for the diagnosis of intervertebral disc protrusion, intraspinal lesions and spinal cord edema.
Note
Before taking a contrast radiograph in animals, a plain radiograph should be taken to match it with the contrast radiograph to get appropriate results.