TABLE OF CONTENTS
Complications of wound
There are various complications of wound- Wound dehiscence, Haemorrhage, Traumatic neuralgia, Septicaemia and pyaemia, Traumatic fever, Haematoma, Sinusitis, Fistula, Cellulitis, Exuberant granulation tissue (proud flesh), Tetanus, Adhesions, Traumatic emphysema, Venous thrombosis, Gas gangrene etc.
Wound dehiscence
Wound dehiscence is the splitting and separation of previously closed wound layers. Evisceration is protrusion of viscera through the wound. Eventration is protrusion of the bowels from the abdomen. The main causes responsible for these conditions include improper surgical technique and the local and systemic factors described below. Dehiscence usually occurs 3-5 days after surgery before collagen deposition. The characteristics features include incisional swelling, discolouration, necrosis and unusual exudation.
Haemorrhage
Haemorrhage due to rupture of blood vessels can lead to development of hemorrhagic shock and ultimately death.
Traumatic neuralgia
Traumatic neuralgia is the pain perceived at or around the vicinity of wound. Primary traumatic neuralgia persist for prolong period whereas secondary one appear during cicatrisation.
Septicaemia and pyaemia
Septicaemia and pyaemia are the common complications of wound healing cause by the bacterial toxins due to massive infection and may lead to endotoxic shock.
Traumatic fever
Traumatic fever is the resultant of pyrogen release from neutrophils and injured body tissue.
Haematoma
Haematoma (accumulation of blood in the Subcutis) or seroma (accumulation of serum in the dead space) may occur due to rupture of blood vessels following injury.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis (draining tract from a suppurative cavity to the surface) may develop due to presence of necrotic tissue debris and foreign bodies.
Fistula
Fistula (abnormal passage between two internal organs) may develop due to paucity of drainage from a purulent cavity.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is inflammation of the connective tissues presenting as oedema, redness, pain and heat often with hardness.
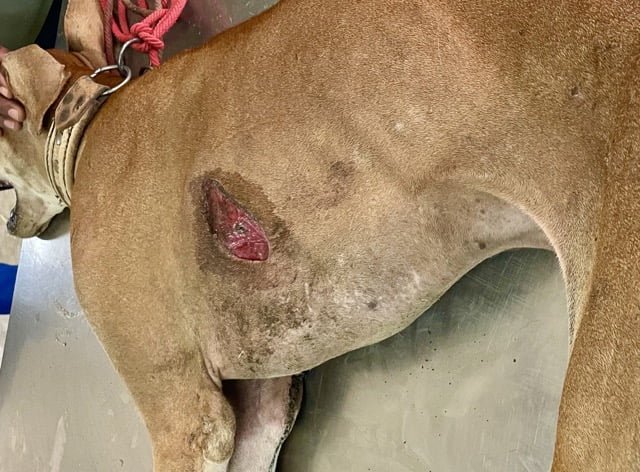
Exuberant granulation tissue (proud flesh)
Exuberant granulation tissue (proud flesh) is granulation tissue which grows above the level of the surrounding skin (overgranulation), preventing epithelial cells from growing across the wound.
Tetanus
Tetanus may develop due to Clostridium tetani infection particularly in deep penetrating and punctured wound. Caprine, equine and camalidae are more susceptible to tetanus.
Adhesions
Adhesions are the major post-operative complication following abdominal surgery due to rough handling of viscera.
Traumatic emphysema
Traumatic emphysema arises due to punctured wounds of the respiratory or gastrointestinal tract where gas or air accumulate in and around the wound area.
Venous thrombosis
Venous thrombosis and embolism may occur when fat tissue accidentally entered in the circulation.
Gas gangrene
Gas gangrene may develop as a part of Complications of wound. Infection with certain types of bacteria, such as clostridium. The bacteria rapidly destroy muscle and surrounding tissue.