TABLE OF CONTENTS
Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone is a Bactericidal, semi-synthetic beta-lactam, third generation cephalosporine antibiotic. It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Group
Ceftriaxone is grouped in Antibiotics.
Mechanism of Action
Ceftriaxone interferes with the cell wall (Peptidoglycan) synthesis. Cell walls are important for the structural integrity of bacteria. Due to cell wall lysis, bacteria swell and burst.
Ceftriaxone is distribute widely including Cerebrospinal fluid / CSF.
Ceftriaxone treats Enterobacteriaceae, Lyme’s disease, Borrelia sp., and gram-negative aerobes, e.g., E. coli, Pasteurella and Salmonella infections, respiratory infections, etc.
Dose Rates
Dogs & Cats: 15-50 mg/kg q12hr IV, SC, IM
Large animals: 10-20 mg/kg q12hr IV,SC, IM
Horses: 25 -50 mg/kg q12hr IV, SC, IM
Poultry: 100mg/kg q4hr IM
Indications
- Respiratory tract infections
- Urinary tract infections
- Soft tissue or skin infections
- Metritis
- Mastitis
- Nephritis
- Endometritis
- Pyometra
- Actinobacillosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Bronchopneumonia
- Black quarter
Contraindications
- In animals that are hypersensitive to penicillin-like drugs, use with caution
- Prolonged treatment in animals should be avoided especially in cats
Interactions
- Concomitant use of aminoglycosides and loop diuretics potentiates the nephrotoxic effects of cephalosporins
- Bacteriostatic (e.g., chloramphenicol) should not be combined with cephalosporins
- Probenecid prolongs plasma levels by competitively inhibiting tubular secretion
Adverse effects
- Oral dose may cause vomiting and diarrhoea
- Hypersensitivity
Toxicity
Ceftriaxone may cause hypersensitivity. It should be treated with steroids or antihistamines and further use should be terminated.
Preparations
Injections: Available in powder form vials
Oral: Oral preparations of Ceftriaxone are not available in India
Potentiated Ceftriaxone
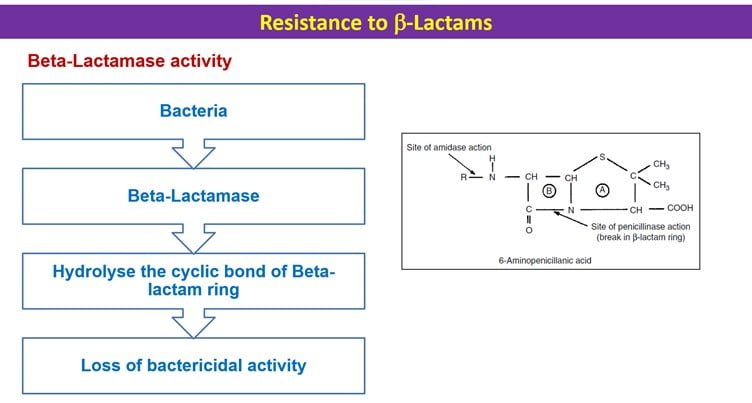
All beta-lactam antibiotics have a beta-lactam ring in their structure. This beta-lactam ring is responsible for antibacterial activity. Some bacteria are able to break this ring by the beta lactamase enzyme. This bacteria is called beta lactam resistant bacteria. For the prevention of the breakdown of the beta lactam ring from resistant bacteria, beta lactamase inhibitors are used. These are clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam.
Potentiated beta-lactam antibiotics are made by combining beta-lactam with beta-lactamase enzyme inhibitors. Ceftriaxone is combined with Sulbactam or tazobactam and called Potentiated Ceftriaxone. This is very effective but expensive then plane Ceftriaxone.
More about Ceftriaxone for animals
Beta lactamase activity of resistance bacteria-
Information provided here may be subject to inaccuracies. Please consult a reputable textbook for verification before use. We welcome your feedback and suggestions for improvement via email at hello@vetscraft.com

