TABLE OF CONTENTS
Canker in Horses
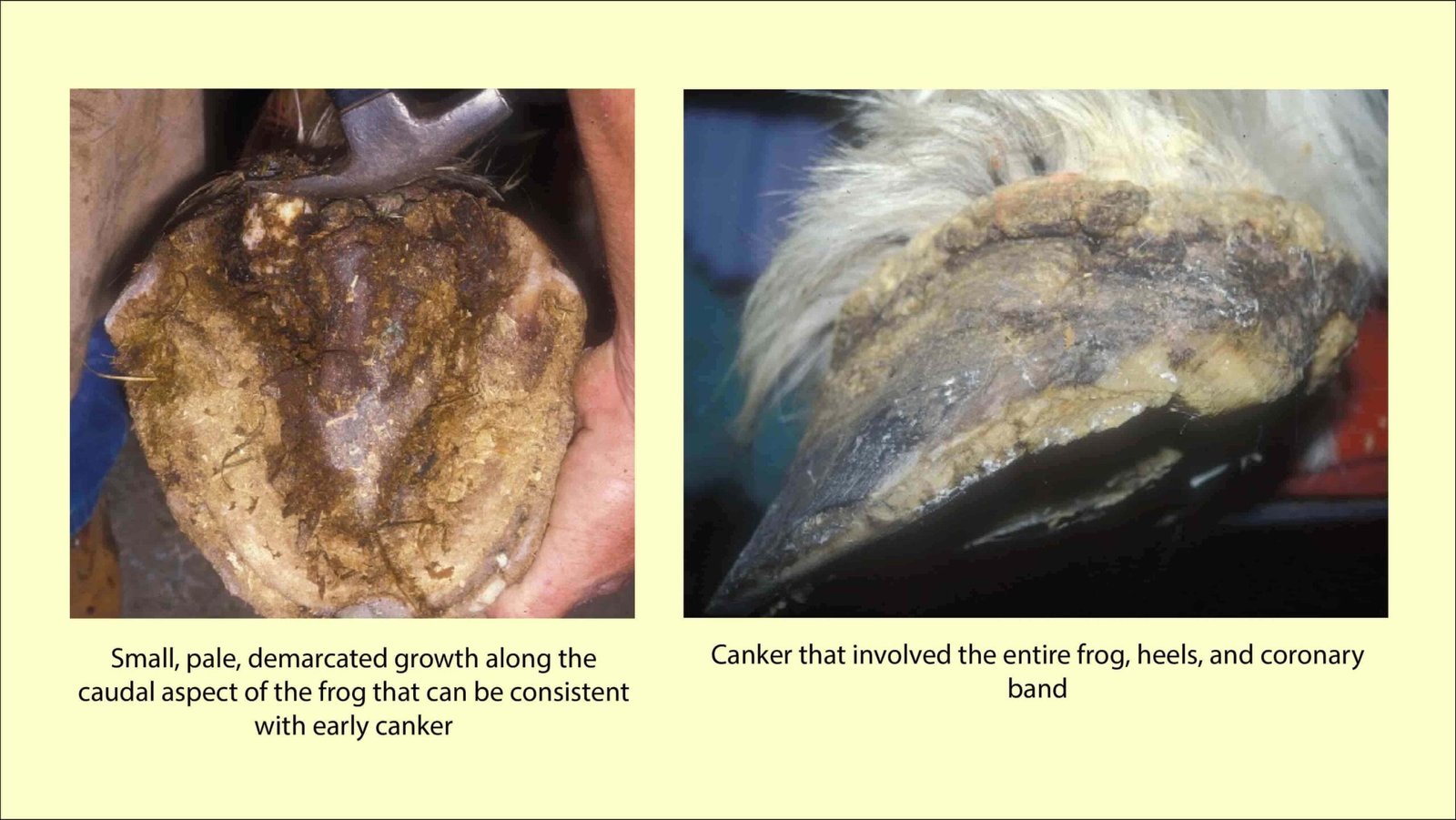
Canker in Horses is a chronic, hypertrophic, moist, eczematous, dermatitis involving the foot. The frog, sole and wall of the foot are affected.
Etiology
- Constant work in mud; dirty, unhygienic condition of the stable etc
- No specific organism is found to be responsible for the condition
- Heredity may be predisposing factor
Canker is more common in the hind feet. Heavy draft horses are more commonly affected.
Symptoms
The horn in the affected areas becomes separated in flakes and is moist as though soaked in oil. In long standing cases the sensitive lamina is exposed.
The sensitive lamina shows hypertrophic changes and become covered with vegetation or finger like hypertrophic papillae and foul smelling caseous exudates.
The lesion may be covered with horn, constituting what are known as ergots.
The lesion is not painful and lameness is not marked except in very severe cases where the where the ospedis is exposed.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Canker in Horses is based on the clinical signs and culture of the microorganism.
Treatment
- Remove the loose horn
- Clean and dress he foot with antiseptic powder. After about 24 hours take away the dressing and remove the loose flakes of horn. An antiseptic dressing like triple sulphate foot dressing (copper sulphate + ferric sulphate + zinc sulphate) is applied
- After the diseased horn has completed sloughed away a less irritant antiseptic like iodoform with zinc oxide is preferable
- The affected portion of sole is protected by a metal or leather sole
- Administration of arsenic as a skin tonic is also advisable
Topical treatments to treat canker include chloramphenicol; metronidazole powder; 2% metronidazole ointment; a mixture of ketoconazole, rifampin and DMSO; and a mixture of 10% benzoyl peroxide in acetone and metronidazole powder.
Canker is a condition that affects the frog and sole of the foot’s horn-producing tissues, causing chronic hypertrophy and an apparent suppuration. There is no known cause. Although it is frequently stated that this illness only affects animals kept in filthy or moist conditions, it can also affect well-cared-for animals.