TABLE OF CONTENTS
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is a Bactericidal, semi-synthetic beta-lactam penicillin antibiotic. It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Group
Amoxicillin is grouped in Antibiotics.
Mechanism of Action
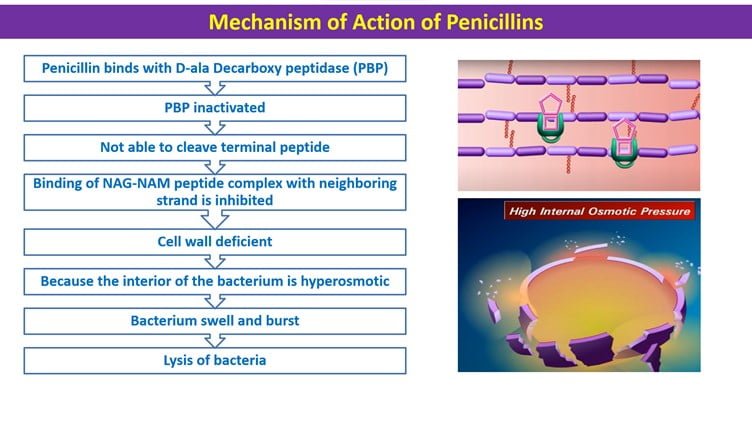
Amoxicillin interferes with the cell wall (Peptidoglycan) synthesis. Cell walls are important for the structural integrity of bacteria. Due to cell wall lysis, bacteria swell and burst.
Amoxicillin act against streptococci, non beta lactamase producing staphylococci, and other gram-positive cocci and bacilli. Many Staphylococcus strains are resistant because of beta-lactamase production. Most enteric gram negative Enterobacteriaceae bacilli are resistant. Susceptible gram negative bacteria include some species of Proteus, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus spp. Resistance among other gram negative bacteria is common.
Dose Rates
- Dogs and Cats : 10-30 mg/kg q12hr IV, PO, SC, IM
- Horse, Cattle, sheep and Goats: 5-20 mg/kg q12hr IV, SC, IM
- Poultry: 10-20 mg/kg q12hr PO by adding to drinking water
Amoxicillin is not advised to be administered through oral administration in large animals since it is poorly absorbed.
Indications
- Respiratory tract infections
- Urinary tract infections
- Soft tissue or skin infections
Contraindications
- In animals that are hypersensitive to penicillin-like drugs, use with caution
Interactions
- Avoid combining with other medications in compounded formulations
- Probenecid prolongs plasma levels by competitively inhibit tubular secretion
Adverse effects
- Oral dose may cause vomiting and diarrhoea
- Hypersensitivity
Toxicity
Amoxicillin may cause hypersensitivity. It should be treated with steroids or antihistamines and further use should be terminated.
Preparations
- Injectables: Powder form preparations available
- Capsules: 250mg, 500mg
- Suspensions: 250mg/5mL
Various Amoxicillin preparations are given below for animals-
- Tab. INTAMOX-O: 1.5gm Amoxycillin trihydrate
Various Potentiated Amoxicillin preparations are given below for animals-
- Inj. Amoxirum Forte: 300mg, 3000mg and 4500mg vials with amoxicillin and salbactum
- Inj. Toxo-mox: 300mg and 600mg vials with amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
- Tab. Toxo-mox: 250mg and 500mg with amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
- Syr. Toxo-mox: 200 amoxicillin + 28.5 clavulanic acid
- Vetzaclav 3600: 3.6gm vial contains amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
Various Amoxicillin combination preparations are given below for animals-
- Inj. INTAMOX: 2.5gm, 3.5gm and 4.5gm vials contains Amoxycillin and Cloxacillin
Potentiated Amoxicillin
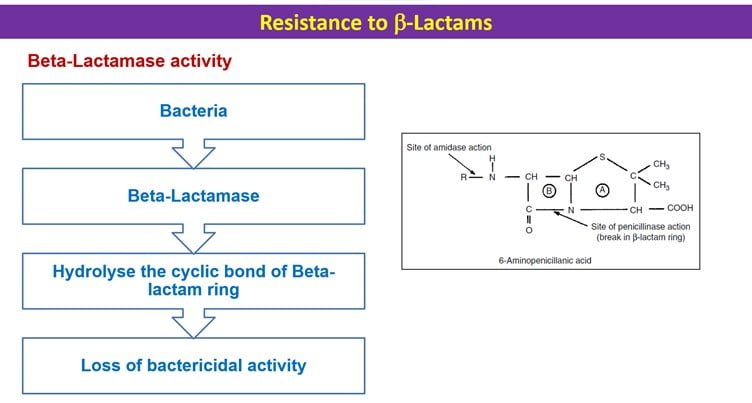
All beta-lactam antibiotics have a beta-lactam ring in their structure. This beta-lactam ring is responsible for antibacterial activity. Some bacteria are able to break this ring by the beta lactamase enzyme. This bacteria is called beta lactam resistant bacteria. For the prevention of the breakdown of the beta lactam ring from resistant bacteria, beta lactamase inhibitors are used. These are clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam.
Potentiated beta-lactam antibiotics are made by combining beta-lactam with beta-lactamase enzyme inhibitors. Amoxicillin is combined with clavulanic acid and called Potentiated Amoxicillin. This is very effective but expensive then plane Amoxicillin.
More about Amoxicillin for animals
Beta lactamase activity of resistance bacteria-
Mechanism of action of Amoxicillin-
Information provided here may be subject to inaccuracies. Please consult a reputable textbook for verification before use. We welcome your feedback and suggestions for improvement via email at hello@vetscraft.com

